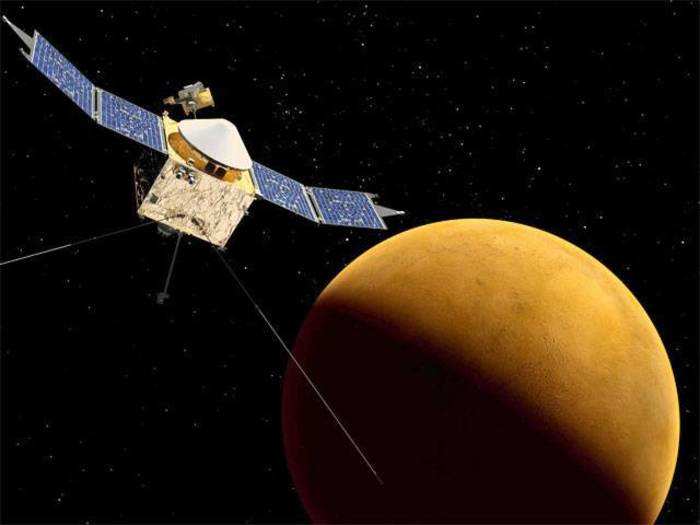






 Stock markets stage strong rebound after 4 days of slump; Sensex rallies 599 pts
Stock markets stage strong rebound after 4 days of slump; Sensex rallies 599 pts
 Sustainable Transportation Alternatives
Sustainable Transportation Alternatives
 10 Foods you should avoid eating when in stress
10 Foods you should avoid eating when in stress
Copyright © 2024. Times Internet Limited. All rights reserved.For reprint rights. Times Syndication Service.