- Home
- cryptocurrency
- news
- Every country wants a piece of cryptocurrency, but how is it benefiting them?
Every country wants a piece of cryptocurrency, but how is it benefiting them?

- Countries like El Salvador are adopting Bitcoin rather than having to rewrite their monetary policy to make international transactions easier.
- Others, like China, Russia, and Turkey, are looking to central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) to counter the US dollar’s dominance.
- Likewise, Iran doesn’t want to be bullied by one superpower and its sanctions.
- Here’s what is driving the crypto revolution around the world and what different countries have to gain by bringing Bitcoin into the mainstream.
The fiat system suited everyone. Despite having its own set of drawbacks like hyperinflation, it has been a reliable solution for decades.
The global financial industry assumes that central banks shall always lend a helping hand via sovereign backing. But these assumptions are now rudimentary in a highly digitised world where even a meme-based cryptocurrency can technically perform international payments without requiring a complex system like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication).
The current evolution of digital currencies can be divided into two categories — decentralised currency like Bitcoin or Ethereum and central bank digital currency (CBDC). The two are pretty distinct but share the same goal of bringing modern-era banking to the average Joe, anywhere.
Here’s how different economies are adopting cryptocurrencies — and why:
For many countries, Bitcoin is a ray of hope
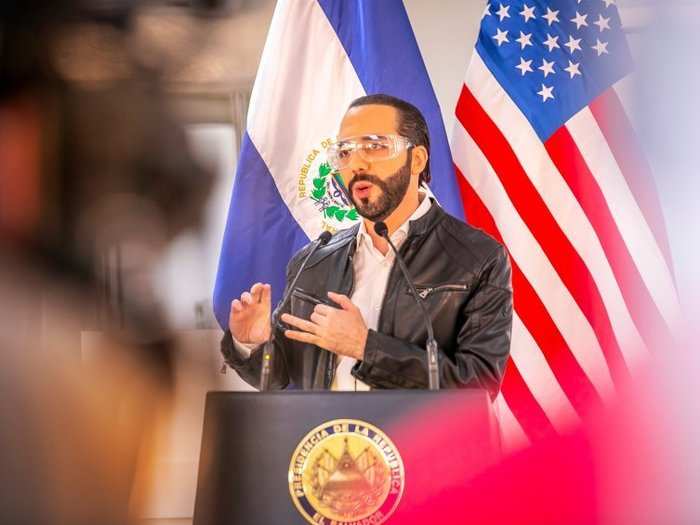

The tiny Central American country of El Salvador has made history by legally recognising Bitcoin as legal tender.
The country's economy is mainly dependent on remittances, requiring a middle-man for forex exchange and international transfers. Every dollar coming into the country loses some of its value due to the long and arduous process.
Since most of the country's residents are not connected to modern banking systems, cash is the ultimate instrument. It further adds stress on an economy that's already dependent on a foreign currency.
Bitcoin can change this by directly enabling offshore transfers, domestic payments, and a modern banking experience. For such a small country, it's a logical step since it can't afford to frame a fashionable monetary policy.
El Salvador’s decision has opened the floodgates for other Latin American countries

Following El Salvador's decision, politicians in the neighbouring countries of Panama, Paraguay, Argentina, and Brazil have voiced their endorsement about such a transition.
Bitcoin is fundamentally a currency for these residents, which can also be considered an asset class due to its future potential. While questions over its blockchain's sustainability continue to haunt the community, it's not a concern in the short term.
Bitcoin is well equipped to handle peer-to-peer payments, and Ethereum 2.0 promises to contribute much more. In a nutshell, cryptocurrencies offer growth and freedom that a fiat currency can no longer deliver due to its saturation point and inherent limitations.
For countries like Iran, cryptocurrency means freedom

The US has put severe sanctions on the Middle Eastern country that has some of the most potent oil reserves in the world. The harsh punishment limits Iran's access to the US dollar, which is the unofficial international standard at the moment.
It has invested heavily in mining farms and leverages its energy to mine as many Bitcoins as possible. Even though mining is temporarily barred due to an energy crisis, the country already has 4.5% of all the Bitcoin hash rate in the world. That's significant for a country that's otherwise known for a conservative culture and governance style.
It hopes that someday, the decentralised currency will help it leap back into a financial system that isn't bullied or controlled by one superpower. For Iran, too, cryptocurrencies are an asset, as well as a currency.
CBDC — a shortcut to supremacy?

Unlike Bitcoin, a CBDC can be e-yuan, e-rupee, or even an e-euro. Instead of printing notes and coins, a central bank can issue digitised tokens. It's a hybrid mix of fiat systems and a modern blockchain, which intends to bring a balance.
A central bank ensures the currency isn't too volatile, solving a problem plaguing Bitcoin and others since their inception. At the same time, it offers maximum flexibility to users as they can spend their money with ease, gradually bringing them onboard an entirely digitised world.
China’s CBDC is a battle for control

China has unveiled a pilot program in Chengdu involving 200,000 people and a 40 million digital yuan ($6.2 million) giveaway by the local government. Six state-owned banks have already rolled out the program, and the country has grand plans of taking over the world by storm.
China already enjoys a lot of influence in south-east Asia, and a cutting-edge currency will further help it counter the dollar influence.
Not to forget, China isn't too pleased with private companies like Alibaba and Tencent controlling the payments industry. Ant Group's cancelled IPO is one strong indication that China may have embraced capitalism, but it hasn't lost touch with its socialist roots.
In a country where every single message is moderated or screened by the Great Firewall, CBDC is a miracle. It offers far more control and individual data to authorities, making it easier for the state to crush dissent or anything it deems unfavourable.
China isn’t alone in its endeavour to counter the dollar’s influence

Russia is also working on e-rubble and even intends to form a cross-border network. Its natural allies currently include China and Turkey, an axis against the dollar.
Crypto innovation is an endearing pitch for even mature economies like the US

The digital concept isn't too draconian, and even healthy democracies are opening up to its vision. Japan, the EU, the US, Singapore, and South Korea are also racing to establish or experiment with CBDCs.
These developed countries have a strong fiat currency, but it won't stay that way if innovation and brainstorming end. Payments are handled mainly by for-profit companies like PayPal, Western Union, and more.
These countries have enough resources to rework their monetary policies at a macro scale and change the future seamlessly. Fiat currencies are still preferred because of their massive fundamental backing — for example, the US Federal Reserve — and relatively little volatility. These same fundamentals can be bridged to back the e-dollar, rendering the charm of Bitcoin powerless in most cases.
Cryptocurrencies are a fresh slate for the economic underdogs

Countries like Nigeria, Ethiopia and Ghana are also discussing the potential of CBDCs, and for them, the purpose is unique. These countries are considered economic underdogs because they have immense potential and are just getting started.
Nobody expects the e-naira to become more potent than the dollar, but nobody also expects their financial system to remain in the old ages either.
The world's wealth distribution is critically imbalanced, and commodities like gold and silver were often plundered from unstable regions to stable ones. These countries are now facing a unique challenge — cling onto the current trend of a robust global dollar or kick start their novel revolution.
They also have their share of unique problems like under-equipped government institutions and large-scale poverty.
To address the plethora of issues, these countries need a custom-made solution that requires hyperlocal reach. Even something as basic as a know-your-customer (KYC) can prove to be difficult due to a lack of documentation. A brand new monetary policy can address these issues, indirectly democratising the otherwise prejudiced financial system.
India already has the NPCI

While the hot buzzword is crypto, India achieved a unique feat a few years ago with the Modi government’s controversial demonetisation move. While the plan did practically nothing to stop the flow of black money, as was promised, it did help digitise India's banking infrastructure unlike any other.
National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), a consortium of state-backed and private banks, created a complex network called the Unified Payments Interface (UPI). It allows peer-to-peer transactions in real-time between any bank account in the country. A truly universal system that has broken all records.
And, the NPCI has been diversifying what it has to offer
NPCI also came up with RuPay, a payments system designed to reduce reliance on foreign players like Visa and MasterCard.
Zero-balance bank accounts became a reality, and soon, government subsidies and payments were directly being transferred electronically. If that wasn't enough, National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) is yet another product by NPCI that provides touch-free toll transactions across India. While NPCI has a monopoly right now, the government is opening up the industry to more players, demolishing a monopoly, and raising the bar.
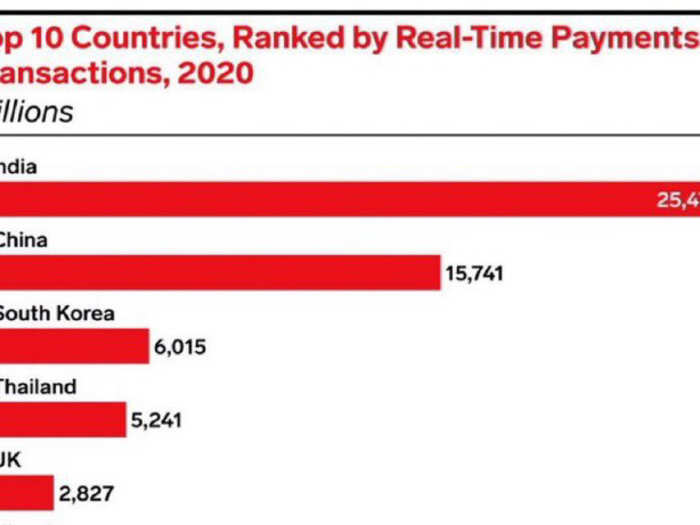
According to a report by ACI Worldwide and GlobalData, India tops the real-time payments industry with more than 25 billion transactions in 2020. It observes that by the year 2025, digital payments in India would collectively account for 71.7% of overall payments volume, taking over cash.
So, what’s the fate of cryptocurrencies in India?

The NPCI is a contributing factor towards the government's reluctance with cryptocurrencies. After decades of building forex reserves, deploying protectionist measures, and direct investment in financial infrastructure, the initial promises of cryptocurrencies fell on deaf ears.
However, the country has also slowly understood the potential of crypto and intends to regulate it somehow. While the details are unknown, the crypto exchanges, think tanks, and experts have strongly suggested considering cryptocurrencies as an asset class.
READ MORE ARTICLES ON
Popular Right Now
Advertisement